Dental bridges are a cornerstone in restorative dentistry, designed to address the gap left by one or more missing teeth. A bridge typically consists of two or more crowns for the teeth on either side of the gap — these are called abutment teeth — and a false tooth/teeth in between.
These false teeth, known as pontics, can be made from a variety of materials, including gold, alloys, porcelain, or a combination of these materials.
Introduction to Dental Bridges
The necessity of replacing missing teeth cannot be overstated. Each tooth in our mouth plays a vital role not just in our ability to chew and speak, but in maintaining the overall structure of our mouth. When a tooth is lost, the balance is disrupted, leading to potential movement of the remaining teeth into the gap.
Read it: Dental Implant Materials
This movement can cause a domino effect, altering the bite, and possibly leading to tooth decay, gum disease, and additional tooth loss. Furthermore, the absence of teeth can lead to bone loss in the jaw, changing the shape of one’s face and affecting one’s speech and appearance.
Dental bridges not only restore the functionality and aesthetics of missing teeth but also prevent the remaining teeth from drifting out of position. By bridging the gap, they ensure the alignment of teeth is maintained, which is crucial for a healthy bite and oral health.
The process of getting a dental bridge usually involves two or more visits to the dentist. Initially, the abutment teeth are prepared by removing a portion of enamel to allow for a crown to be placed over them. Impressions of the teeth are then made, which serve as a model from which the bridge, pontic, and crowns will be made by a dental lab.
A temporary bridge will be set in place to protect the exposed teeth and gums while the bridge is being made.
Choosing the right type of dental bridge depends on several factors, including the location of the missing tooth (or teeth), the health of the abutment teeth, and personal preferences regarding materials and budget.
The decision-making process is crucial and requires thorough consultation with a dental professional to ensure that the chosen solution effectively restores the function and appearance of missing teeth while preserving oral health.
In summary, dental bridges offer a durable and aesthetically pleasing solution to the problem of missing teeth. They play a crucial role in restorative dentistry, helping patients regain their smile, confidence, and the functional use of their teeth, all the while preventing further oral health issues.
Innovations in Dental Bridge Materials
The realm of dental restoration has witnessed significant material advancements, particularly in the domain of dental bridges. One notable innovation is the introduction of Advanced Gold Technology (AGT) in Captek bridges.
This development stands at the forefront of modern dental solutions, offering an unmatched combination of superior fit, bond strength, and aesthetic advantages. These advancements have set new standards in dental restorations, ensuring patients receive the best in both functionality and appearance.
Advanced Gold Technology in Captek Bridges
Captek bridges, leveraging AGT, represent a pinnacle in restorative dentistry materials. AGT is not your traditional gold; it is a culmination of years of research and technological advancements in metallurgy.
The technology utilizes a high-purity gold compound that is engineered to provide enhanced physical properties compared to standard dental materials. This innovative material offers exceptional durability and biocompatibility, making it an ideal choice for patients.
Superior Fit and Bond Strength
The precision and adaptability of Captek bridges with AGT are unparalleled. The material’s unique composition allows for a fit that closely mimics the natural structure of the teeth. This precision in fit not only improves the comfort and functionality for the patient but also significantly reduces the risk of decay under the bridge.
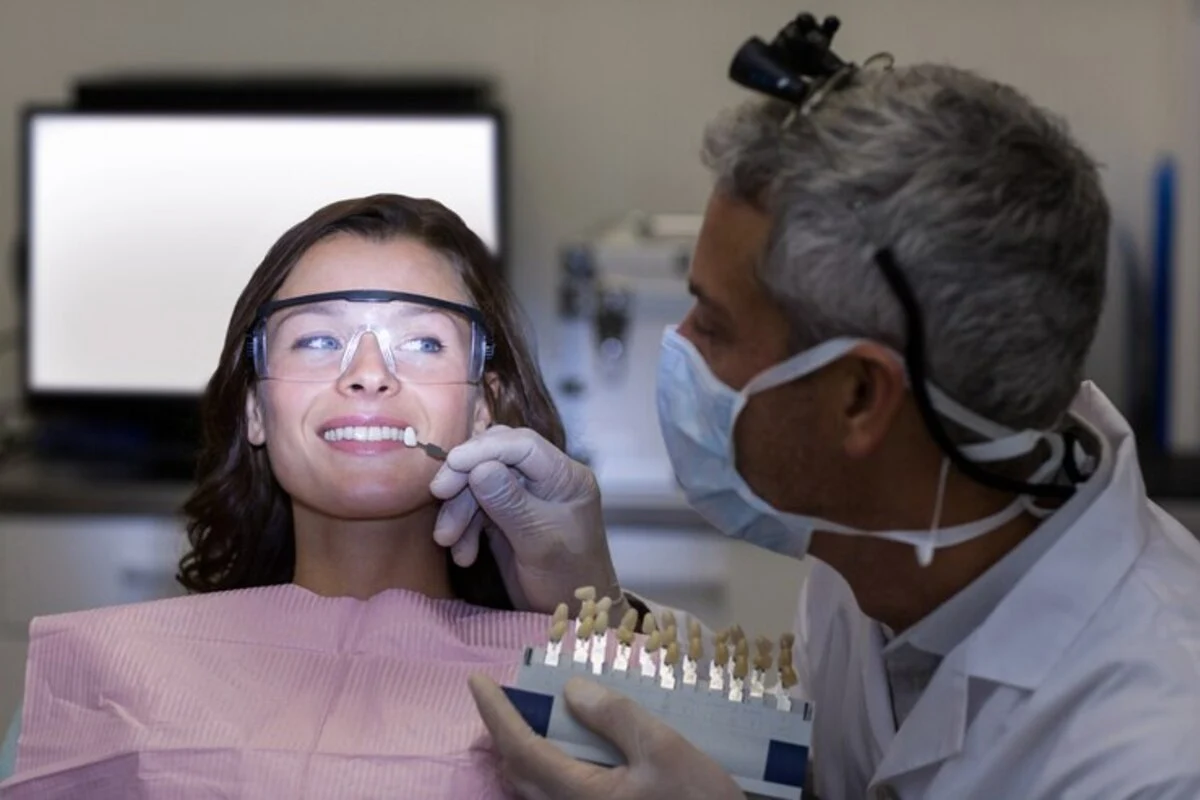
Moreover, the bond strength of AGT is a game-changer. It ensures that the bridge remains securely in place, offering reliability and peace of mind for both the dentist and the patient.
Aesthetic Advantages
Aesthetic considerations are paramount in dental restorations. Captek bridges with AGT shine in this regard, offering a natural, radiant appearance that blends seamlessly with the patient’s existing teeth.
The material’s ability to replicate the luster and translucency of natural teeth allows for restorations that are virtually indistinguishable from the real thing. Patients can smile confidently, knowing their dental bridges enhance not only their oral health but also their overall appearance.
Conclusion
The innovations in dental bridge materials, exemplified by the introduction of Advanced Gold Technology in Captek bridges, mark a significant leap forward in dental restorative solutions.
These advancements not only enhance the functional aspects of dental bridges but also elevate the aesthetic outcomes to new heights. As the field of dentistry continues to evolve, the focus on combining cutting-edge technology with patient-centric solutions remains paramount. The future of dental restorations looks bright, with materials like AGT leading the way in providing durable, aesthetically pleasing, and highly functional dental bridges.
Technological Breakthroughs Enhancing Dental Bridge Procedures
The field of dentistry is witnessing a remarkable transformation, thanks to technological breakthroughs that are enhancing dental bridge procedures. These innovations are not only revolutionizing the way dental professionals approach restorations but are also significantly improving patient experiences.
Among these advancements, 3D printing, digital impressions, and laser dentistry stand out for their ability to offer custom solutions, precision, and comfort.
3D Printing for Custom Solutions
3D printing technology has emerged as a game-changer in dental bridge procedures. Its ability to produce custom dental implants and bridges tailored to the unique contours of a patient’s mouth ensures a perfect fit and natural appearance. This precision significantly improves the functionality and longevity of dental bridges, making them more comfortable and effective than ever before.
The rapid prototyping capabilities of 3D printers also mean that patients can receive their custom bridges much faster, reducing wait times and the number of dental visits required.
Read it: Advances in Dental Crown Techniques
Digital Impressions for Enhanced Accuracy
Gone are the days of uncomfortable trays filled with impression material. Digital impressions have revolutionized this process, making it more comfortable and significantly more accurate. Using a handheld scanner, dentists can now capture detailed 3D images of a patient’s teeth and gums.
These digital models are then used to design and fabricate dental bridges with unprecedented precision. This technology not only eliminates the discomfort associated with traditional impressions but also reduces the margin for error, ensuring that the final restorations fit perfectly.
Laser Dentistry for Precise Treatment with Minimal Discomfort
Laser dentistry is another technological innovation making dental bridge procedures more precise and less invasive. By using lasers to remove diseased or damaged tissue, dentists can prepare the teeth for bridges with unparalleled accuracy, preserving more of the healthy tooth structure.
Lasers cause less trauma to the surrounding tissues, resulting in minimal discomfort and faster healing times for patients. Additionally, the precision of laser dentistry means that treatments are more effective and efficient, enhancing the overall quality of care.
Together, these technological advancements are setting new standards in dental care. They represent a significant leap forward in the ability to provide patients with dental bridges that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional and comfortable.
As these technologies continue to evolve and become more integrated into dental practices, patients can look forward to even better outcomes and experiences. The future of dental bridge procedures is bright, with these innovations leading the way toward more effective, efficient, and patient-friendly treatments.
Future Directions and Challenges
The landscape of restorative dentistry is on the brink of a new era, propelled by advancements in materials, technology, and treatment methodologies. These innovations aim to enhance treatment outcomes, elevate patient satisfaction, and promote the preservation of healthy dental tissue.
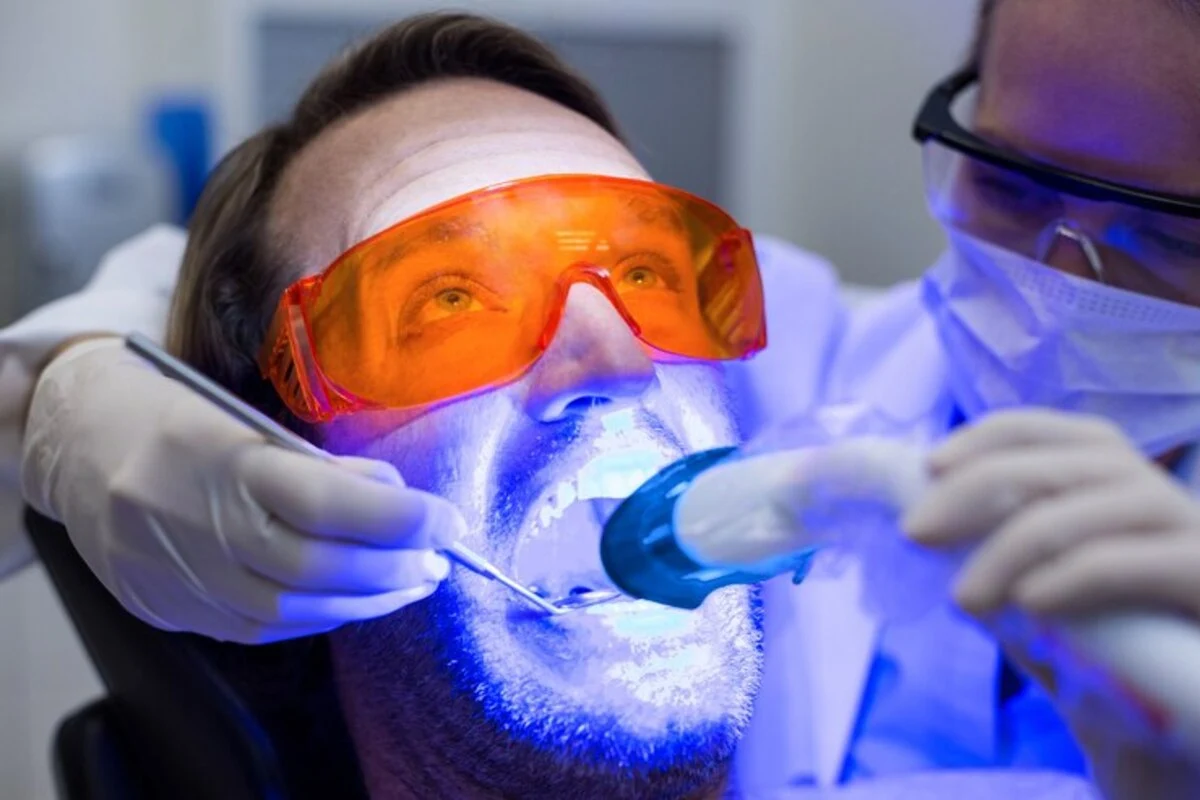
The integration of digital workflows, CAD/CAM systems, and minimally invasive approaches is setting the direction for future developments. However, while these advancements promise significant benefits, they also bring forth challenges related to clinical effectiveness and outcomes.
Digital Workflows and CAD/CAM Systems
The adoption of digital workflows and CAD/CAM systems in restorative dentistry has revolutionized the design and fabrication of dental restorations. These technologies allow for precise and efficient production of dental prosthetics, including bridges, crowns, and veneers, tailored to the specific anatomical features of each patient.
The result is restorations that offer superior fit, function, and aesthetics. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can anticipate even more sophisticated solutions that further streamline the restoration process and improve the patient experience.
Minimally invasive dentistry emphasizes the conservation of healthy tooth structure, focusing on prevention and the use of the least invasive treatment options. Techniques such as air abrasion, laser dentistry, and biomimetic restorations are at the forefront of this approach, offering alternatives to traditional methods that often require more extensive tooth preparation.
By preserving more of the natural tooth, these techniques support long-term dental health and reduce the need for more significant interventions in the future.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising advancements, several challenges remain. One of the primary concerns is ensuring the clinical effectiveness of new materials and techniques. As the field continues to innovate, rigorous clinical trials and long-term studies are essential to validate the safety, reliability, and durability of new restorative solutions.
Additionally, there is the challenge of accessibility; advanced technologies and materials can be costly, potentially limiting their availability to a broader patient population.
Another consideration is the learning curve associated with new technologies. Dentists and dental technicians must acquire new skills and adapt to evolving practices to effectively utilize digital tools and minimally invasive techniques. This necessitates ongoing education and training within the dental profession to ensure that practitioners can deliver the highest standard of care using the latest advancements.
Looking Ahead
The future of restorative dentistry holds great promise, with continuous innovations aimed at improving patient care and treatment outcomes. As the field navigates the challenges and embraces the opportunities presented by new technologies and approaches, collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and industry partners will be key.
Read it: Full Mouth Reconstruction
Together, the dental community can overcome obstacles and advance restorative dentistry to new heights, enhancing the oral health and well-being of patients around the world.
As restorative dentistry continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technologies and materials with a minimally invasive ethos represents a balanced approach to dental care, promising a future where restorations are not only effective and aesthetic but also increasingly aligned with the natural biology of the oral environment.

