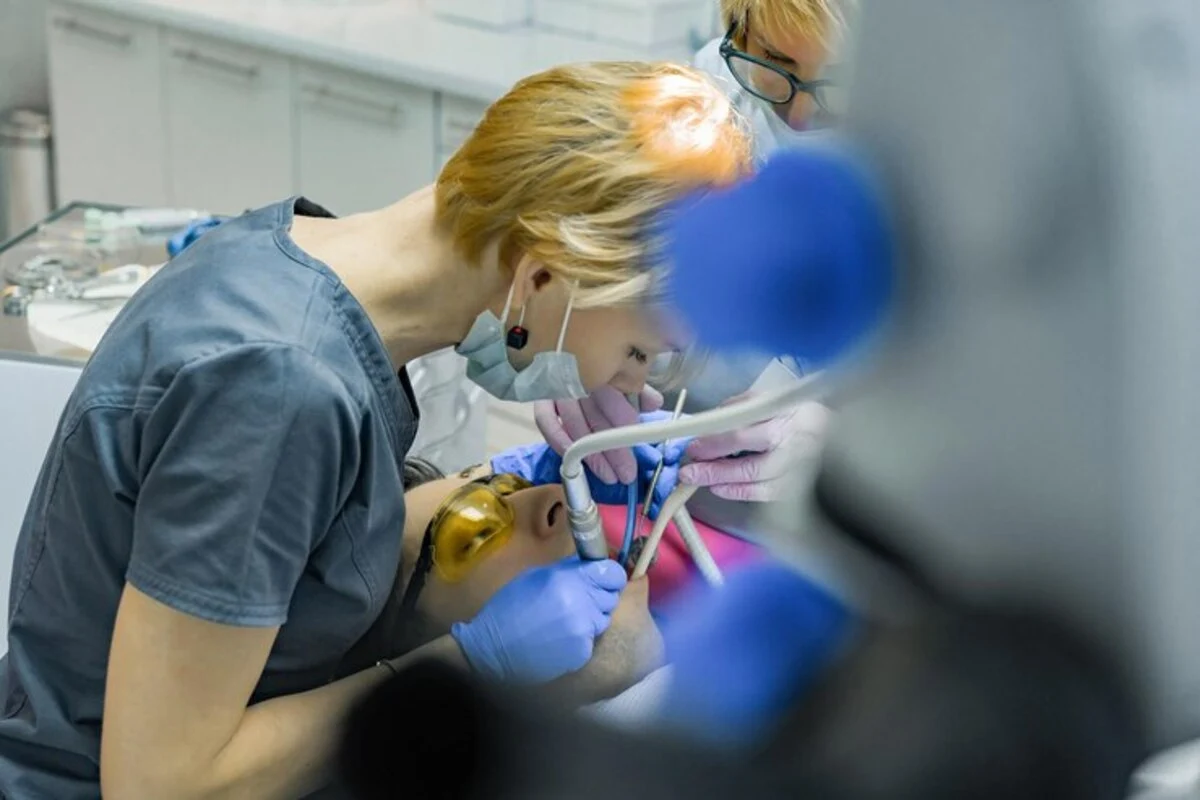
The intersection of biomimetic and holistic dentistry represents a transformative approach to dental care, one that harmonizes the restoration of dental health with the overarching well-being of the individual.
This introduction unfolds the foundational principles and synergies between these two realms, setting the stage for a comprehensive understanding of their significance in modern dental practice.
Introduction to Biomimetic and Holistic Dentistry
Biomimetic dentistry emerges from the aspiration to emulate the natural form and function of teeth within the restorative process. This approach leverages advanced materials and techniques to mimic the biomechanical, aesthetic, and functional properties of natural dentition.
The objective is to restore teeth in such a way that the interventions are indistinguishable from the natural tooth structure, both in appearance and performance. This method underscores the importance of conservation, aiming to maintain as much of the original tooth structure as possible, thereby preserving its vitality and preventing further interventions such as root canals.
Holistic dentistry, on the other hand, extends the scope of dental care to consider the patient’s total health. It operates on the premise that oral health is intrinsically linked to the overall health of the body and mind. Holistic practitioners prioritize biocompatible materials, eschew the use of toxic substances such as mercury, and employ minimally invasive techniques.
Their goal is to ensure that dental treatments do not adversely affect other parts of the body, adhering to the principle that dental care should contribute positively to the patient’s overall health and well-being.
The convergence of biomimetic and holistic dentistry offers a paradigm that is greater than the sum of its parts. By combining the meticulous emulation of natural tooth properties with a comprehensive view of the patient’s health, this integrated approach delivers dental solutions that are not only effective in addressing specific dental issues but also conducive to the patient’s general health.
This dual focus not only enhances the longevity and functionality of dental restorations but also aligns dental interventions with the body’s natural processes and the individual’s holistic health objectives.
Moreover, this approach champions the use of materials and procedures that are in harmony with the body’s natural chemistry and physiology.
Biomimetic restorations, crafted from materials that closely replicate the physical and aesthetic qualities of natural teeth, are integrated within a holistic framework that assesses the biocompatibility and systemic impact of these materials. This ensures that restorative treatments bolster oral health without compromising the body’s overall ecological balance.
In essence, the fusion of biomimetic and holistic dentistry marks a significant evolution in dental care, one that respects the intricate relationship between oral health and the body’s systemic health.
By foregrounding the principles of natural emulation and holistic well-being, this approach not only redefines the standards of dental restoration but also reaffirms the role of dentistry in nurturing the complete health of the individual.
Advancements in Biomimetic Materials and Techniques
The realm of biomimetic dentistry has seen significant advancements in materials and techniques that have fundamentally shifted the approach to dental restorations.
These developments aim not only to replicate the appearance of natural teeth but also to restore their intrinsic properties, such as strength, flexibility, and resilience to wear and tear.
Materials that Mimic Nature
Central to the biomimetic approach is the use of materials that closely resemble the composition and properties of natural tooth enamel and dentin. Composite resins have been refined to offer improved wear resistance and aesthetic qualities that mimic the translucency and gloss of natural teeth.
These materials are not only used for fillings but also for inlays, onlays, and veneers, providing a durable and visually appealing restoration option.
Read it:
Meet the Fortune Smiles Dental Care Team
Porcelain, another key biomimetic material, has been enhanced through nanotechnology to improve its strength and aesthetic properties. The latest generations of ceramic materials are capable of mimicking the light-reflecting properties of natural teeth, making them an ideal choice for crowns and bridges.
Techniques for Natural Restoration
In addition to material advancements, biomimetic dentistry employs techniques that preserve more of the tooth’s natural structure. Adhesive dentistry has revolutionized the way restorations are bonded to the tooth, using adhesives that integrate with the tooth’s molecular structure to create a seamless and strong bond.
This reduces the need for extensive tooth preparation, preserving more of the natural tooth and maintaining its integrity.
Layering techniques have also been refined to replicate the natural gradation of colors and translucency found in tooth enamel. By applying materials in layers, dentists can recreate the subtle variations in color and translucency that characterize individual teeth, leading to restorations that are virtually indistinguishable from natural dentition.
Preservation of Tooth Vitality
A hallmark of biomimetic dentistry is its emphasis on preserving the vitality of the tooth. Techniques such as minimally invasive caries removal and the use of biocompatible materials help maintain the health of the tooth pulp.
By avoiding extensive drilling and the use of materials that can cause thermal or chemical irritation, biomimetic dentistry reduces the risk of complications such as tooth sensitivity and necrosis.
The Role of Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in the advancements of biomimetic dentistry. Digital imaging and CAD/CAM (computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing) systems allow for precise mapping and fabrication of restorations that fit perfectly with the natural tooth structure.
This precision ensures that restorations not only look natural but also function harmoniously with the bite and jaw movements.
Laser dentistry is another technological advancement supporting biomimetic principles. Lasers can be used for a variety of procedures, including cavity preparation and gum reshaping, with minimal discomfort and without the need for traditional drills. This technology supports the biomimetic goal of preserving natural tissue and promoting healing.
Looking Forward
As biomimetic dentistry continues to evolve, ongoing research and innovation in materials science and dental techniques promise even more effective and naturalistic restorations. The future may see the development of bioactive materials that can actively contribute to the healing and regeneration of dental tissues, bringing the field closer to its goal of perfectly mimicking nature.
The advancements in biomimetic materials and techniques represent a significant leap forward in dental care, offering patients restorations that not only look natural but also preserve the function and health of their teeth.
As these technologies continue to develop, the gap between natural and artificial will become ever narrower, ensuring that restorations contribute to overall oral health in a holistic manner.
The Synergy between Biomimetic Practices and Holistic Health Principles
The fusion of biomimetic dentistry with holistic health principles heralds a new era in dental care, one where the restoration of dental function and aesthetics goes hand in hand with the promotion of overall well-being.
This synergy is rooted in a shared emphasis on minimal intervention, the use of biocompatible materials, and a deep respect for the body’s natural ability to heal.
A Shared Vision for Minimally Invasive Care
At the core of both biomimetic and holistic dentistry is the commitment to minimally invasive care. This approach seeks to preserve as much of the natural tooth structure as possible, recognizing that the best outcomes are achieved when interventions are conservative and targeted.
By minimizing the removal of healthy tooth material and avoiding procedures that can stress the tooth, such as extensive drilling or the use of heat-generating equipment, these practices work in concert to maintain the integrity and vitality of the tooth.
Biocompatibility: A Cornerstone of Synergy
Biocompatibility is another key area where biomimetic and holistic dentistry converge. The selection of materials that are compatible with the body’s natural tissues is paramount in both disciplines. Biomimetic dentistry’s focus on materials that closely mimic the properties of natural teeth complements the holistic approach’s emphasis on avoiding substances that could be harmful to the body.
Read it: Preventative Dentistry
This mutual priority ensures that restorations do not introduce potential toxins or allergens into the body, supporting the patient’s overall health and wellness.
Holistic Health: Beyond the Mouth
Holistic dentistry expands the scope of care to consider the patient’s overall health status, lifestyle, and well-being. This broader perspective aligns with biomimetic dentistry’s goal of creating restorations that function harmoniously within the oral ecosystem.
The holistic approach recognizes that oral health is interconnected with systemic health; for example, inflammation in the mouth can affect other parts of the body. By integrating biomimetic principles, holistic dentistry can provide treatments that not only address dental issues but also contribute to the patient’s general health.
Read it: Dental Material in Holistic Dentistry
Enhancing Healing and Regeneration
The integration of biomimetic practices within a holistic framework also opens avenues for enhancing natural healing and regeneration. Biomimetic techniques that promote the preservation of tooth pulp and encourage the natural healing of tissues are complemented by holistic methods such as nutritional support, stress reduction, and the use of natural remedies.
These combined strategies foster an environment conducive to healing, supporting the body’s innate regenerative capacities.
The Role of Patient Education and Empowerment
A crucial element of the synergy between biomimetic and holistic dentistry is the emphasis on patient education and empowerment. Both disciplines advocate for patients being informed participants in their care, understanding the options available and the implications of their choices.
Read it: Full Mouth Reconstruction
Education on the importance of oral health, its impact on systemic health, and the benefits of minimally invasive, biocompatible treatments empowers patients to make decisions that align with their health goals and values.
Looking Forward
As we look to the future, the integration of biomimetic and holistic principles in dentistry promises to further revolutionize dental care. Innovations in materials and techniques, along with a growing understanding of the oral-systemic health connection, will continue to drive this evolution.
The ultimate goal is a model of dental care that is not only effective in treating dental diseases but also promotes the overall health and well-being of the patient.
In conclusion, the synergy between biomimetic practices and holistic health principles represents a holistic approach to dentistry that is more than the sum of its parts. By marrying the technical innovations of biomimetic dentistry with the broad health perspective of holistic practices, this integrated approach offers a path to dental care that is aligned with the body’s natural processes, supports systemic health, and empowers patients to take an active role in their wellness journey.
Future Perspectives: Innovations and Challenges in Integrating Biomimetic Dentistry within a Holistic Framework
The integration of biomimetic dentistry within a holistic framework is paving the way for future innovations in restorative dentistry, with both fields emphasizing a patient-centered approach that aligns closely with the body’s natural processes. Biomimetic dentistry focuses on restoring teeth to their natural state by using materials and techniques that mimic natural tooth structure, function, and aesthetics.
This discipline has seen significant advancements, particularly in the development of materials that closely resemble the biomechanical and aesthetic properties of natural teeth, such as advanced composites and ceramics enhanced through nanotechnology.
One of the key innovations in biomimetic dentistry is the use of non-collagenous protein analogues and ion-releasing materials to achieve functional remineralization of enamel and dentin. This approach aims to replicate the prismatic structure of enamel and achieve interfibrillar mineralization in dentin, which could significantly enhance the durability and performance of restorative materials.
Furthermore, the application of biomimetic principles in clinical endodontics, including tissue engineering strategies for dental pulp regeneration, highlights the potential for biomimetic approaches to extend beyond restorative dentistry into other areas of dental care.
Despite these advancements, integrating biomimetic dentistry within a holistic framework presents several challenges.
The complexity of accurately replicating the natural properties of dental tissues, ensuring long-term durability of restorative materials, and the need for extensive clinical validation are among the hurdles that must be overcome. Additionally, there is a growing need for dental professionals to receive specialized training in biomimetic techniques to fully leverage these innovations in clinical practice.
Looking forward, the convergence of biomimetic and holistic dentistry holds the promise of more effective, less invasive, and biologically harmonious dental treatments.
As research continues to evolve, we can anticipate further innovations in materials science and therapeutic approaches that will enhance the ability to preserve and restore natural tooth structure, while also considering the patient’s overall health and well-being.
This holistic approach to dental care not only has the potential to improve oral health outcomes but also to positively impact systemic health, reinforcing the intrinsic connection between oral health and general health.

